In 1905 Albert Einstein explained how it was possible that light would be measured the same for all observers no matter the speed of the light source. It was a triumph of perspective - the facts were all there but took an Einstein to put it all together.
Special Relativity is a collection of facts about how things act when traveling near the speed of light. It is "Special" because it only deals with objects traveling at a constant velocity. Special Relativity introduces "SPACETIME" to our vocabulary - the three dimensions of space and the dimension of time are all related to each other and measurements of spacetime can vary depending on perspective.
It's SPECIAL because it is limited to constant velocity
Now united as one, space and time affect each other
We live in 3 spacial dimensions and one time dimensionj
"At rest" = ANY constant velocity
If you can't tell the difference by experiment, there is no difference
No longer constants - now dependent upon velocity
but only from an external perspective
everything looks normal from inside
It took Einstein another decade to figure out how to extend his Special Theory of Relativity to objects that are doing more than just moving at a constant velocity. This is called his General Theory of Relativity.
If there is no internal experiment that can be done to differentiate among a high constant velocity, a low constant velocity, or "rest" - those states must be equivalent.
In the same way, if there is no internal experiment that can be done to differentiate among a gravitational field and acceleration, those states must be equivalent. But first back to Newton and his Law of Universal Gravitation.
Let's compare you in a rocket (far from earth) accelerating "up" at 9.8 m/s/s and you in a rocket-shaped room on the surface of earth in a gravitational field of 9.8 N/kg.
If you can't tell the difference between the two with an internal experiment, they must be the same.
One crazy conclusion is that acceleration of an object and the effect of a gravitational field are equivalent. Let's do another experiment using a laser or a beam of light in an accelerating rocket.
Fire that laser under a massive acceleration and both internally and externally you would see a curved beam. The floor is moving toward the point of origin of the beam of light.
Remember that equivalence principle - acceleration and g-field are the same so everything that would happen under a huge acceleration...
Here's where Einstein's twisted mind comes in again. If gravity attracts light and bends it but light has no mass, how does it do that?
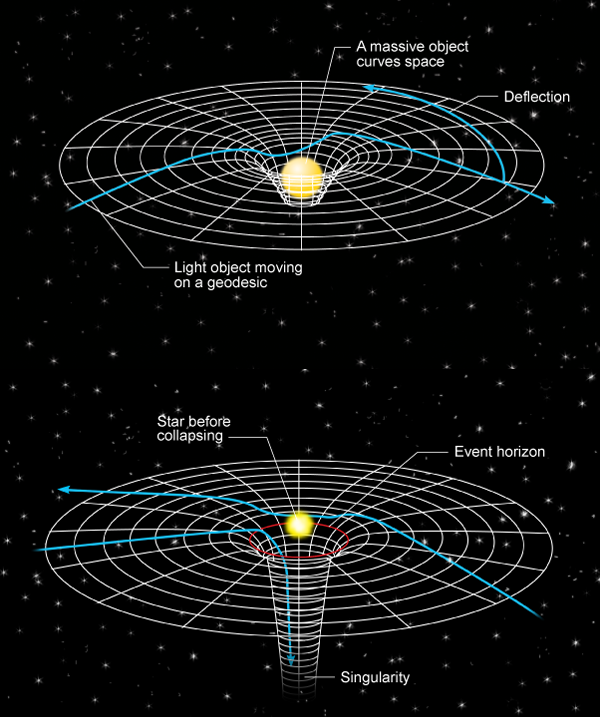
That pesky spacetime again must be affected not only by relative velocities but by large concentrations of mass and gravitational fields and accelerations.
Mass bends time. An atomic clock in orbit around earth runs faster than the same one on earth. Even more slowly at the surface of our sun. And even more slowly near a black hole.
Ridiculous. Even more ridiculous is that light is bent when near a big mass like our sun. It was during a solar eclipse in 1919 that scientists took pictures of the stars around the sun and found a star that should not have been visible. The light had been bent by the gravitational field near the surface of the sun - the first experimental verification of Einstein's General Theory of Relativity.
BUT - Einstein again - the light isn't the thing that is bent. Spacetime is bent and light follows a straight line.
And remember that gravity- acceleration equivalence principle again - the same would happen under acceleration - Acceleration bends spacetime too so that twin paradox isn't a paradox, it just depends on the bending of spacetime under acceleration (gravity field).
That "twin paradox" from last time depends on the acceleration/gravity field effects of General Relativity.
Einstein's twisted mind again. This time with more math.